Test Parameters Determination
The first and most important step is to determine the test parameters for the product while performing the leak tests of a product in the production stage. For this, we must first know the type of fluid to which the product to be tested is exposed. What is the fluid expected to be sealed in the product? | Gas (Air, vacuum, O2, N2, CO2, …) | Liquid (Water, oil, fuel, …)
Glass Bottle Helium Example
Consider a glass bottle that is theoretically sealed with a hermetically sealed cap. It is a suitable sealing material if we use a glass bottle to store water. But it’s also permeable to helium gas unless it’s an engineered, custom-made glass bottle. From this example, we can deduce that the words “leakproof” or “0 leaks” must be well-defined. The leakproof is the amount of leakage at an acceptable rate, which is decided according to the predetermined parameters.
What Should Be Considered When Determining Test Parameters?

What are the consequences if a leak occurs?
In this question, we can divide the results into 3 groups. The products in the first group consist of products that are low in price and do not threaten human health in case of leakage.

The products in the second group consist of products that are costly but not life-threatening. If your action camera, which you bought for its waterproof feature, breaks down while rafting, it will break your spirit. However, this situation does not pose a risk that will affect living life.
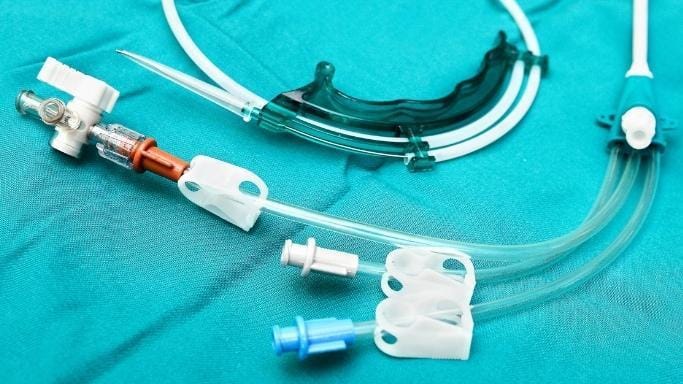
The products in the third group consist of products that are independent of their cost and that could be life-threatening in case of leakage. You don’t want the fuel hose of your car or the catheter to be used in your heart surgery leaking.
In which environmental conditions will the product be used?
Leakage tests should be performed at the product’s usage temperature range and usage pressure.
What is the expected time for the product to operate at high performance?
Packages used in the food and beverage industry can be expected to remain sealed for 1-2 years. Manometers are expected to remain sealed for up to 1 million cycles and to measure accurately.
Leak-proof Expected Scenarios
- Liquids coming out of the product (Beverage, Medical Catheter, Fuel Hose)
- Liquids entering the product (Electronic Products, City Pipelines)
- Exhaustion of gases from the product
- Hazardous gases (Home, Nerve Gas, Combustible Gases)
- Non-hazardous gases (Vehicle Tires, Building Ventilation Pipes, Helium Cylinders)
- Bacterial contaminations (Drugs, Medical Products, Food&Beverage, Cosmetics)
How is The Leakage Rate Test Parameter Determined?
The most commonly used method is to set parameters using the flow rate formed at the test pressure. The problem that arises at this point is the unit confusion that will occur if the leakage flow rate is calculated in m3/s. Consider 2 Laminar flows with the same flow velocity in volume but at different pressures. Although it has the same volume/s flow rate in high-pressure flow, the number of molecules passing through the hole and the amount of leakage throughout the flow will be higher.
If we look from the perspective of the perfect gas law, PV=nRT, that is, the pressure and temperature of the fluid are among the important factors affecting its volume. For accurate determination of the leak rate, sccm is used. 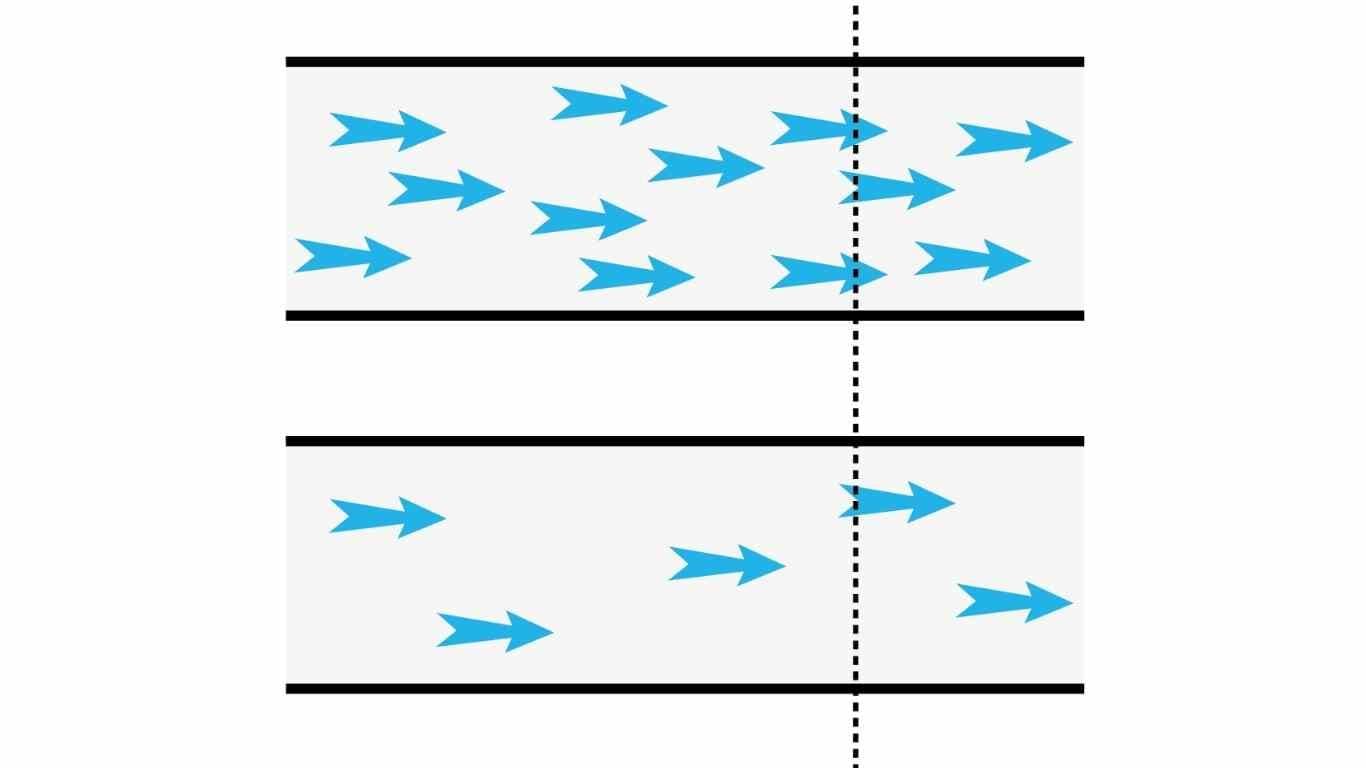 1 cm³ mass flow per minute of the defined fluid at normal conditions at 1 ATM pressure and 0°C is defined as 1sccm. Sccm is a measure of molar flow rate (kmol/s). The other method is to calculate the holes in the product. In this method, the hole size is determined by calculating the type of flow over the roughness of the surface and the test pressure.
1 cm³ mass flow per minute of the defined fluid at normal conditions at 1 ATM pressure and 0°C is defined as 1sccm. Sccm is a measure of molar flow rate (kmol/s). The other method is to calculate the holes in the product. In this method, the hole size is determined by calculating the type of flow over the roughness of the surface and the test pressure.
Theoretical Calculation of Maximum Leakage Rate while Determining Test Parameters
When working with a unique or previously untested product, it is theoretically possible to calculate the maximum leak rate. Let’s say we want the tire pressure to decay to a working pressure of 3 bar at the end of 1 year, through leaks, to be a maximum of 0.2 bar. We can calculate the maximum leakage rate in sccm that we will use for the test parameter over the annual pressure decay. It is critical that the material used is hydrophilic or hydrophobic.
The thing we need to know about our product, which we tested with air, is that even if there are many small pores in the material, water cannot pass through these holes at pressures below the surface tension, but air can. The important thing to know when testing at pressures below surface tension is the size and number of pores/holes in the product.
Porous Materials When Determining Test Parameters
Various fabrics used in medical masks, sportswear, or various materials such as wine cork are porous but do not allow liquid passage. In these cases, since the surface tension of the liquid is greater than its weight, or in other words, the force it exerts on the surface, the material used becomes leakproof for the liquid in question. 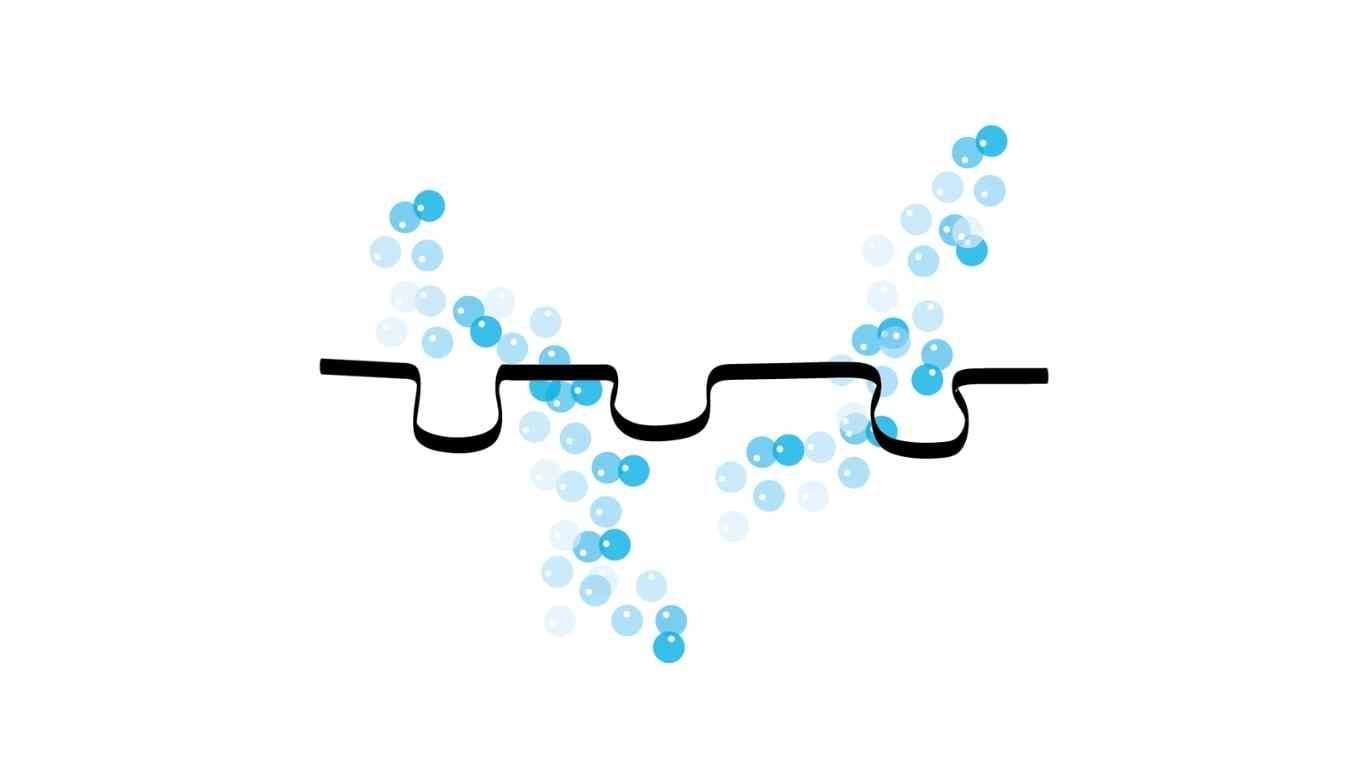
Since the surface tension effect is low in large-sized holes, it leaks water.
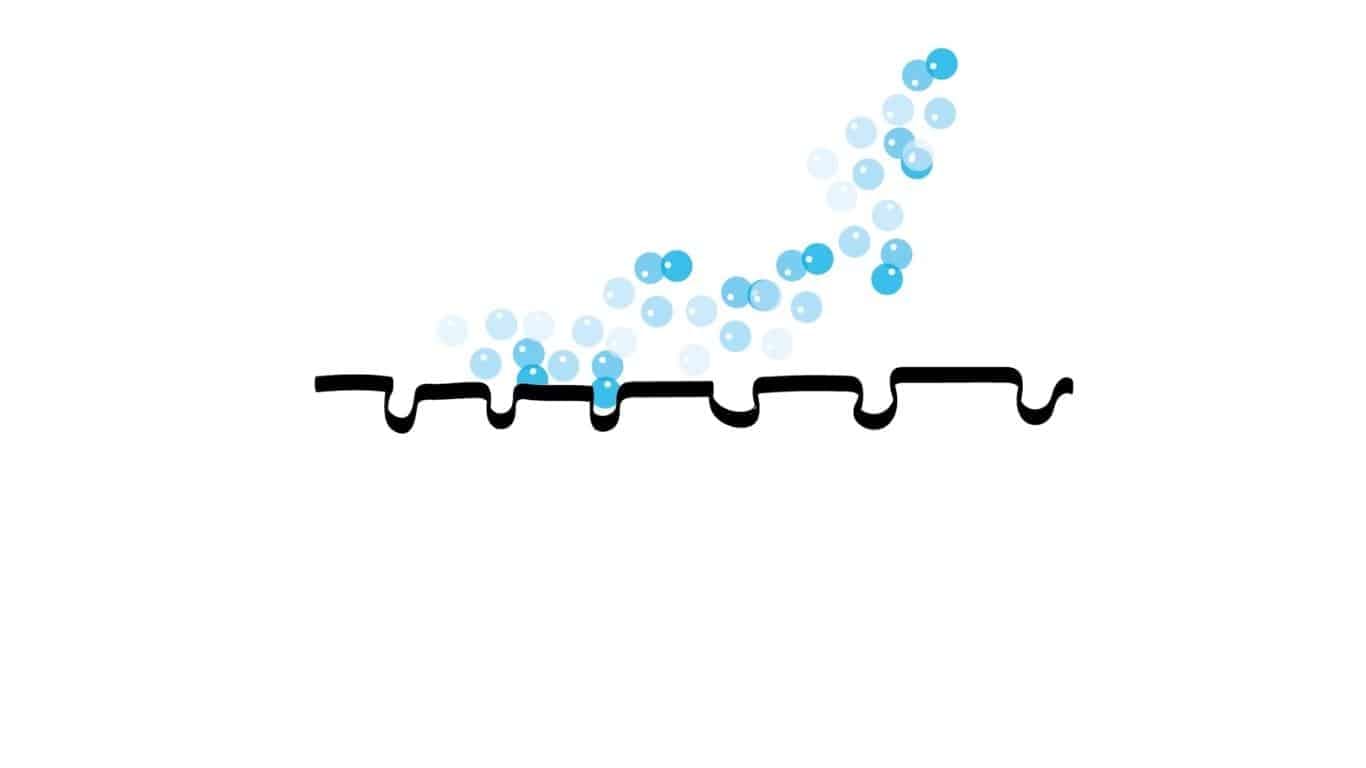
Since the surface tension effect is high, it does not leak water.
Comparing with Faulty Products and Bubble in Water Method
Celebrating theoretical methods for deciding test parameters is appropriate but not sufficient. Although the calculated leak parameters can be obtained with Adlema leak testers, sample parts must also be tested in water to compare test parameters.
The reason for making these comparisons while determining the parameters is to fine-tune the parameters. It is not sustainable to apply very low leakage parameters. Although the leak test increases the investment cost in the first stage, it is not possible for the manufacturers to meet the production methods that will follow these strict parameters. It is ideal to choose test parameters that are suitable for the product, are viable in terms of sustainability, and are safe.
After the acceptable test parameters suitable for the product have been determined, the next step is to select the method and the device that can perform the tests in these parameters.


